Pomegranate farming in Kenya is slowly gaining attention among farmers who want to invest in high-value crops. Pomegranate, also known locally as Kukumanga, is one of the most expensive fruits in the Kenyan market.
The fruit has a bright red color, juicy seeds, and a rich nutritional profile. It is highly sought after for its medicinal and health benefits. Despite its potential, only a few farmers in Kenya grow pomegranate, making it a rare but profitable venture.
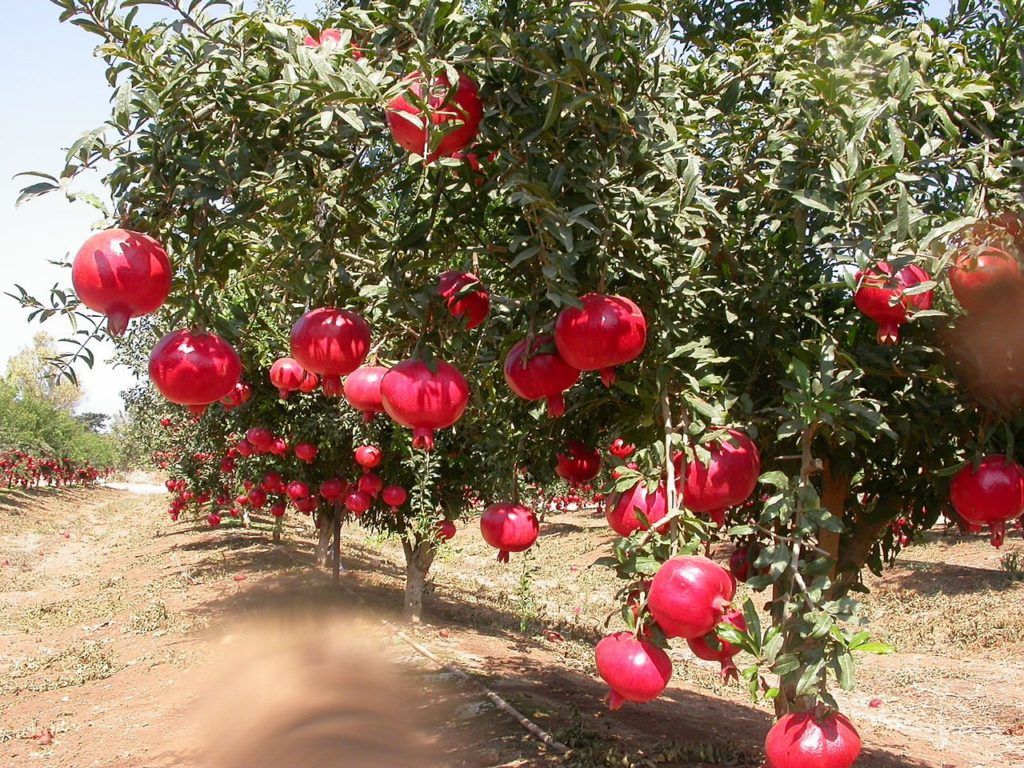

Pomegranate Farming In Kenya
Pomegranate farming in Kenya is a smart choice for farmers in arid and semi-arid areas. The fruit thrives in dry regions where many other crops struggle to grow. With its resilience and high market price, pomegranate offers an opportunity for farmers to diversify their sources of income.
Nutritional Benefits of Pomegranate
Kukumanga is one of the healthiest fruits you can grow and consume. It is packed with nutrients that boost human health.
- It is rich in dietary fiber which improves digestion.
- The fruit contains nitrates that enhance blood flow.
- It has anti-inflammatory properties that help fight diseases.
- Flavonoids in pomegranate counteract cancer-causing cells.
- It reduces the effects of dental plaque due to its antibacterial qualities.
- It is an excellent source of Vitamin C and Vitamin K.
With these benefits, demand for pomegranate continues to grow both locally and globally.
Areas Suitable for Pomegranate Farming In Kenya
Pomegranate farming in Kenya is most suitable in dry and semi-dry regions. The crop is drought tolerant and can survive with minimal rainfall. Some of the key areas where it is grown include:
- Makueni
- Machakos
- Kitui
- North Eastern parts
- Nyeri
- Kisumu regions
- Coastal counties
- Parts of Western Kenya
These areas provide the warm climate and soils needed for successful production.
Ecological Conditions for Growing Pomegranate
For profitable pomegranate farming, the right ecological conditions are essential.
- The best temperature range is 20°C to 30°C.
- During flowering and fruit ripening, the optimum is 35°C to 38°C.
- The ideal altitude is between 500 to 1000 meters above sea level.
- The soil should be well-drained with a pH of 6.5 to 7.5.
- Deep loamy soils give the best results.
Since the fruit does not require heavy rainfall, it is ideal for dry regions of Kenya.
Varieties of Pomegranate in Kenya
Farmers in Kenya can grow different varieties of pomegranate depending on availability. Some of the most common ones include:
- Bhagwa
- Jalore Seedless
- Kandhari
- Ganesh
- Jyothi
- Mradula
- Phole Arakta
These varieties differ in fruit size, taste, and seed hardness, giving farmers options to suit market demand.
Propagation and Planting of Pomegranate
Pomegranate is mainly propagated through stem cuttings. Farmers should use healthy cuttings to ensure strong plants. The recommended spacing is 3.5m by 4m. With this spacing, an acre of land can accommodate about 200 plants.
Weeding is necessary in the early stages. Mulching and cover crops can help control weeds and retain soil moisture. Intercropping with other crops is also possible.
Harvesting of Pomegranate
Patience is needed when farming pomegranate since it takes time to mature. The crop starts bearing fruit in 3 to 5 years. Harvesting is done 5 to 6 months after flowering. Farmers should handle the fruits carefully to avoid bruising, which lowers their market value.
Market Opportunities for Pomegranate in Kenya
The market for pomegranate in Kenya is promising. Currently, most pomegranates used for food processing, beauty products, and juice making are imported. Local production can easily fill this gap.
In major towns such as Nairobi, pomegranate fruits sell for Ksh 150 to Ksh 300 each. Seedlings cost around Ksh 300 per plant. This shows the high value of the crop. With proper marketing, farmers can sell directly to markets, supermarkets, and processors.