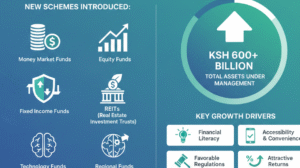
Microfinance banks have become an important part of Kenya’s financial system, giving thousands of low-income earners access to loans, savings, and other essential services.
These institutions help fill the gap left by commercial banks by reaching the unbanked population, especially small entrepreneurs and the unemployed. Licensed and regulated by the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK), these banks play a vital role in driving economic growth, reducing poverty, and supporting small businesses.
As of 2025, there are 14 licensed microfinance banks in Kenya, each contributing uniquely to financial inclusion across the country.

Licensed Microfinance Banks Driving Financial Inclusion in Kenya
Microfinance banks were established to serve individuals and small enterprises excluded from traditional banking systems. They offer affordable loans, savings products, money transfers, insurance, and remittances that support financial independence and entrepreneurship.
These institutions also help build a saving culture among Kenyans, enabling low-income earners to access credit for school fees, business expansion, or emergencies. By focusing on community-level operations, microfinance banks boost economic participation in rural and urban areas alike.
Unlike commercial banks, microfinance banks tailor their services to meet the needs of micro and small enterprises. Their simple account opening processes, flexible collateral requirements, and personalized financial education make them an important tool for promoting inclusive economic growth.
List of All Licensed Microfinance Banks in Kenya
The Central Bank of Kenya periodically updates its list of licensed microfinance banks. Below is the latest official list of institutions operating legally in the country in 2025:
| No. | Name of Microfinance Bank | Date Licensed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Branch Microfinance Bank Limited | 17.09.2012 |
| 2 | Caritas Microfinance Bank Limited | 02.06.2015 |
| 3 | Choice Microfinance Bank Limited | 13.05.2015 |
| 4 | Faulu Microfinance Bank Limited | 21.05.2009 |
| 5 | Kenya Women Microfinance Bank PLC | 31.03.2010 |
| 6 | LOLC Microfinance Bank PLC | 31.12.2010 |
| 7 | Muungano Microfinance Bank Limited | 30.10.2019 |
| 8 | On It Microfinance Bank Limited (formerly Maisha Microfinance Bank Ltd) | 21.05.2016 |
| 9 | Rafiki Microfinance Bank Limited | 14.06.2011 |
| 10 | Salaam Microfinance Bank Limited | 08.11.2010 |
| 11 | SMEP Microfinance Bank PLC | 14.12.2010 |
| 12 | Sumac Microfinance Bank Limited | 29.10.2012 |
| 13 | U & I Microfinance Bank Limited | 08.04.2013 |
| 14 | Umba Microfinance Bank Limited | 12.01.2015 |
This list confirms that Kenya’s microfinance sector continues to expand, attracting new players and encouraging innovation in financial products tailored to underserved populations.
Contribution of Microfinance Banks to Kenya’s Economy
Microfinance banks in Kenya have done more than provide small loans. They have supported entrepreneurship, promoted financial literacy, and reduced economic inequality.
For instance, Kenya Women Microfinance Bank has empowered thousands of women to start and grow businesses. Similarly, Faulu and Rafiki Microfinance Banks have built a strong presence among small traders and farmers.
Many of these banks also invest in digital solutions, offering mobile and online banking to reach remote areas. Branch Microfinance Bank and Umba Microfinance Bank are leading in digital lending platforms that allow users to access loans and savings products directly from their phones.
The combined effort of these banks strengthens Kenya’s Vision 2030 goals by promoting access to credit, job creation, and inclusive growth.
Future Outlook for Microfinance Banking in Kenya
The future of microfinance banking in Kenya looks promising. With technology adoption and improved regulatory frameworks by the Central Bank of Kenya, these institutions are expected to grow stronger and more efficient.
Government initiatives to enhance financial inclusion will also support the sector’s expansion, especially in rural and underserved regions. As more people embrace digital banking, microfinance institutions will continue to bridge the financial gap between formal and informal economies.
Overall, licensed microfinance banks in Kenya remain a cornerstone of the nation’s economic resilience. They represent a lifeline for millions of Kenyans striving for financial independence and improved livelihoods.